SQL Server Joins
Joins in SQL server are used to query (retrieve) data from 2 or more related tables. In general tables are related to each other using foreign key constraints.
A JOIN clause is used to combine rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them.
In SQL server, there are different types of JOINS.
- CROSS JOIN
- INNER JOIN
- OUTER JOIN
Outer Joins are again divided into 3 types.
- Left Join or Left Outer Join
- Right Join or Right Outer Join
- Full Join or Full Outer Join
Cross Join: - Return Cartesian product of the
tables involved in the join.
Inner Join: - Return only the matching rows. Non
matching rows are eliminated.
Left Join: - Return all the matching row + non
matching row from the left table.
Right join: - Return all the matching row + non
matching row from right table.
Full Join: - Return all row from both tables,
including the non-matching row.
Now let's understand all the JOIN types, with
examples and the differences between them.
Employee Table
Department Table
SQL Script to create Employee and Department
tables
Create table Department ( Dep_Id int primary key identity(1,1), Department_Name varchar (50), Location varchar (50), Department_Head varchar (50) ) Create table Employee ( Emp_Id int primary key identity(1,1), Name varchar (50), Gender varchar(50), Salary int, Department_Id int references Department(Dep_Id) ) insert into Department values('IT','London','Rick') insert into Department values('Payroll','Delhi','Ron') insert into Department values('HR','New York','Ravi') insert into Department values('Other Department','Mumbai','Pratik') insert into Employee values('Top','Male',20000,1) insert into Employee values ('Pam', 'Female', 3000, 3) Insert into Employee values ('John', 'Male', 3500, 1) Insert into Employee values ('Sam', 'Male', 4500, 2) Insert into Employee values ('Todd', 'Male', 2800, 2) Insert into Employee values ('Ben', 'Male', 7000, 1) Insert into Employee values ('Sara', 'Female', 4800, 3) Insert into Employee values ('Valarie', 'Female', 5500, 1) Insert into Employee values ('James', 'Male', 6500, NULL) Insert into Employee values ('Russell', 'Male', 8800, NULL) select * from Department select * from Employee
General Formula for Joins
SELECT ColumnList FROM LeftTableName JOIN_TYPE RightTableName ON JoinCondition
CROSS JOIN
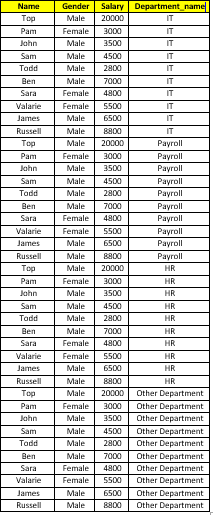
CROSS JOIN Query:
select Name,Gender,Salary,Department_name from Employee cross join Department
OUTPUT
JOIN or INNER JOIN
Write a
query, to retrieve Name, Gender, Salary and DepartmentName from Employees and
Departments table. The output of the query should be as shown below.
Query for retrieving Name, Gender,
Salary and DepartmentName from Employees and Departments.
select Name,Gender,Salary,Department_name from Employee INNER JOIN Department on Employee.Department_Id=Department.Dep_Id
OR
select Name,Gender,Salary,Department_name from Employee JOIN Department on Employee.Department_Id=Department.Dep_Id
Note: JOIN or INNER JOIN means the same. It's always better to use INNER JOIN, as this explicitly specifies your intention.
If you look at the output, we got only 8 rows, but in the Employees table, we have 10 rows. We didn't get JAMES and RUSSELL records. This is because the DEPARTMENTID, in Employees table is NULL for these two employees and doesn't match with ID column in Departments table.
So, in summary, INNER JOIN, returns only the matching rows between both the tables. Non matching rows are eliminated.
LEFT JOIN or LEFT OUTER JOIN.
Now, let's say, I want all the rows from the Employees table, including JAMES and RUSSELL records. I want the output, as shown below.
Query for retrieving all the row from Employees.
select Name,Gender,Salary,Department_name from Employee Left Outer JOIN Department on Employee.Department_Id=Department.Dep_Id
OR
select Name,Gender,Salary,Department_name from Employee Left JOIN Department on Employee.Department_Id=Department.Dep_Id
Note: You can use, LEFT JOIN or LEFT OUTER JOIN. OUTER keyword is optional.
LEFT JOIN, returns all the matching rows + non matching rows from the left table. In reality, INNER JOIN and LEFT JOIN are extensively used.
RIGHT JOIN or RIGHT OUTER JOIN
I want, all the rows from the right table. The query output should be, as shown below.
Query for retrieving all the row from Right table.
select Name,Gender,Salary,Department_name from Employee Right Outer JOIN Department on Employee.Department_Id=Department.Dep_Id
OR
select Name,Gender,Salary,Department_name from Employee Right JOIN Department on Employee.Department_Id=Department.Dep_Id
Note: You can use, RIGHT JOIN or RIGHT OUTER JOIN. OUTER keyowrd is optional.
RIGHT JOIN, returns all the matching rows + non matching rows from the right table.
FULL JOIN or FULL OUTER JOIN
I want all the rows from both the tables involved in the join. The query output should be, as shown below.
Query for retrieving all the row from both table.
select Name,Gender,Salary,Department_name from Employee full Outer JOIN Department on Employee.Department_Id=Department.Dep_Id
OR
select Name,Gender,Salary,Department_name from Employee full JOIN Department on Employee.Department_Id=Department.Dep_Id
Note: You can use, FULL JOIN or FULL OUTER JOIN. OUTER keyword is optional.
FULL JOIN, returns all rows from both the left and right tables, including the non-matching rows.













No comments:
Post a Comment